January 27, 2009
by Hutch Carpenter
Recently, I’ve had former colleagues from a couple of my old employers ask me about social media. Specifically, how to get started in it from a professional perspective. They’re aware that social media can be powerful, but it can be daunting to figure out an entrance point and what you’re supposed to do with it.
[tweetmeme source=”bhc3″]
Now I’m no Chris Brogan, but I do have hands-on experience. Specifically, I’ve been doing product marketing for a while now, with both Connectbeam and BEA Systems. BEA Systems was great for traditional product marketing work. Connectbeam is great for social media-oriented product marketing work. I’ve learned some things that work for me.
In that spirit, I’m going to share them here. Here’s a summary of what follows:
- What is product marketing? messaging, customers, market trends, market visibility
- Leverage the work you’re already doing
- The 9 social media tools I’m using
- Twitter – narrate your work
- Blog – part product, part big ideas
- FriendFeed – tracking the flow
- SlideShare, Scribd – the post-webinar bang-for-your-buck
- YouTube, Google Video – incremental exposure
- Wrapping up – feel free to contact me
OK, let’s get to it.
What Exactly Is Product Marketing?
In the graphic below, I’ve put together a rough (and incomplete) map of the different functions one finds inside companies:

I look at product marketing as having four primary goals:
- Positioning and messaging of the company’s products
- Steady voice and knowledgeable source for customer inquiries
- Staying on top of evolving requirements and ideas in the market
- Establishing the company in the market, with coverage among sources of information used by customers
I want to distinguish product marketing from other functions. Every function can use social media for its benefit, but the use cases vary. For instance, I’d expect engineering to use social media to tap peers who can help with coding or architecture questions.
But let’s be clear what product marketing is supposed to do. It is an outward-facing function, with a number of responsibilities:
- Articulate the value of the company’s products
- Create messaging around the products, via website content, data sheets, white papers, presentations, etc.
- Develop the business case for products
- Put on webinars
- Give customer presentations and demos
- Do market and competitive analysis
The tools of the trade include: data sheets, white papers, newsletters, PowerPoint presentations, Camtasia demos, WebEx/GoToMeeting, trade show booths.
So how does social media play in all this?
Leverage the Work You’re Already Doing
The nice thing about traditional product marketing work is that a lot of it complements social media nicely:
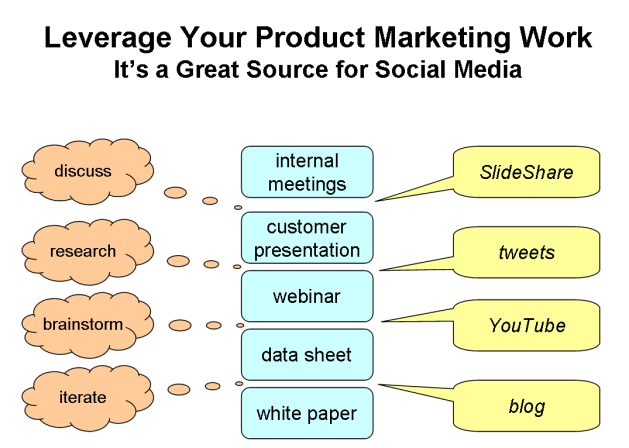
The first bit of advice I want to impart is that if you treat social media like a foreign language, it will be. If you’re wondering where to start, look no further than the thinking and content you already do as a part of your job. That’s plenty good for starting.
There are three activities that the product marketer will engage in:
- Monitor: who is saying what of interest
- Engage: interact with customers, analysts, consultants, competitors
- Broadcast: create content, tweet original thoughts, post to SlideShare, etc.
In the sections that follow, you’ll see all three activities described.
Social Media: What I’m Doing
The tools: Here are the social media tools I use for product marketing:
Changes in latitude, changes in attitude: Attitude is the most important consideration. If you look at the various social media as a pain-in-the-ass part of your job, you’re likely not going to get much from it. It will be too much of a chore for you.
To excel at product marketing, you’ve got to be good at research and building persuasive arguments, along with a personality that engages customers well. It’s really not that hard to extend those traits into social media. And once you read a bit more below, I think you’ll see the value of engaging in social media.
Be a mensch: Do not spend your time running down competitors. It makes you look petty, and you’ll find yourself in entanglements with them which make no one look good. Focus on what your company is about.
Not tonight honey, I have a headache: I’m an ‘I’ introvert on the Myers Briggs test. Which means I tend to reflect on things. There are times I just don’t feel like twittering. And that’s OK. Because there are times I’m fired up. I will rattle off a series of tweets and dive into deeper conversations. Strike while the iron is hot.
Twitter
Twitter is the microblogging platform, and is my most valuable information source for tracking what’s happening in my industry. It’s really quite a simple platform, but it has a tremendously flexible set of use cases.
The basics: Here a few basics about the service:
- 140 characters – learn the power of distinct thoughts in a limited space
- Follow – you see the tweets of whomever you follow, and anyone following you might see your tweets
- @Replies – the @Replies tab serves as an inbox of public tweets meant for your attention. Start a tweet with @[username] and it will end up in that inbox
- RT – stands for retweet. When someone tweets something you like and you want your own followers to see it, you type ‘RT’ , then paste the tweet (with the @[username] included) and hit update.
- DM – Direct Messages are essentially emails, limited to 140 characters. People use them all the time for private conversations.
Fill out your bio: Make sure you do the following with your Twitter account: use your real name, put your location, have a website of some type (your personal blog, company blog, company website), tell who your company is and what you do there, and upload a picture. This seems like basic advice, but if you don’t, a lot of people won’t follow you back. Which makes your product marketing job that much harder.
Also, before you start following people, get 3-4 tweets on your account so you don’t look like a spam bot.
Subscribe: You need to find others to follow on Twitter, otherwise it’s a lonely place. But who? Here a three tips to get started:
- Find prominent bloggers in your space, find their twitter account, and follow them
- Look at who the prominent bloggers are following, and follow the same people
- Run a search on twitter for industry jargon, see if those people are interested in your sector. Click here to go to twitter search.
A lot of those you follow will follow you back. This is how you start growing your own base of followers.
Narrate your work: Great, so you’re set up. Now what to tweet? Lunch menu? Here’s one idea. Narrate your work. Technology legend Dave Winer wrote this idea, and I like it. Tweet what it is you’re doing. But, let’s examine this a bit more.
Do not tweet, “Opening up Microsoft Word” or “Heading into a meeting”. Yes, that’s your work, but it’s nothing anyone cares about. Rather, you might be reading a good article about something relevant to your industry. You like it? Tweet it! A simple tweet like this is great:
Reading: [article name] [shortened URL] [optional – a bit of personal color]
Because of the 140 character limit, typical article URLs are too lengthy for a tweet. Use a URL shortener, like bit.ly. And if you have a pithy thought on the article, tack it on at the end of the tweet.
@reply to people: When someone you’re following tweets something of interest to you, engage them. Ask follow-up questions, agree with them, challenge them. This is the type of thing that puts you “on the map” in Twitter. Done well, you will gain new followers by doing this. Just avoid being a troll. When people @reply to you, make sure you give them the courtesy of a reply back.
Broadcast: Once you’ve established credibility and a set of followers on Twitter, don’t be afraid to broadcast updates. These may be product releases, blog posts, new white papers, conferences you’ll be attending, etc. All that is fine. Unless that’s all you’re tweeting. Then it’s not fine.
And don’t be bashful tweeting successes.
Be an information hub: One observation about @reply tweets. They are the conversational currency of Twitter. Personally, I want to make sure maybe 60% of my tweets are conversational. But I don’t want them too high. As a product marketer, you’ve got a message to impart. Nothing wrong with creating tweets that others like. What are some non-@reply tweets? Retweets, passing along links to interesting information, personal observations as you do your work, or personal life things (such as funny things about your kids).
People will be attracted to twitters who pass along valuable info.
Blog
Check any job description for product marketing, and you’ll see that good writing is a requirement. We do this for data sheets and white papers. And these papers we write are for public consumption. Of course, they do tend to have a fairly structured approach.
Which is what’s nice about blogging. You’re still writing. But the format restrictions of “official” documents are loosened. Language is less formal, you can inject personality and include pictures, videos, polls etc.
What to write: On the Spigit blog, I like to mix it up. I will cover product releases. But I won’t just re-state the data sheets or press releases. I write more of the background, the “why” for a product release or feature.
I cover larger issues as well. This is particularly important for smaller companies. When you’re smaller, you don’t get automatic attention the way Google, Microsoft or Oracle do. That means just writing about your product will result in people not reading your blog posts.
But what do smaller companies have? A different way of looking at the market, and the advantage of generally being more leading edge. For instance, this Spigit blog post, Eight Principles of Enterprise Innovation Management, clearly describes what the burgeoning field covers.
Bloggers love links: When you write these company blog posts, link to other bloggers. For your readers, it’s a great way to show how your thinking ties into issues others are grappling with. For yourself, it’s a good way to memorialize a post you liked. And in case you didn’t know, bloggers love links.
When you link to another blogger, they get a notification of that link. In terms of attention, this is even better than an email. It means you took the time to read their post, and built on it. See who the industry thought leaders are, subscribe to and read their blogs via Google Reader and incorporate their analysis, opinion and observations in your blog posts.
Foreshadow things that are coming up: You know your product roadmap: the features and timing. Prior to those releases, get some posts out that lay down the rationale for the releases. Not in some ham-handed fashion, but as a thoughtful look at the problems or opportunities there are. Pull in research, include excerpts from articles and other bloggers. You then have a good basis for announcing the new features.
Practice makes perfect: Don’t wait until you’ve got a sense of what the perfect blogging style is. Just get in there and do it. You’ll learn over time what subjects resonate, and how to craft an argument that gets attention.
Engage those who comment: People will leave comments on your blog. Make sure you take the time to respond to them. That’s a good way to ensure they come back, and you’ll learn something from the exchange. It also leaves a trail of commentary for others to read.
Blogs are a source of high quality traffic: The Spigit blog is a source of traffic to the Spigit website. Not the biggest, but a meaningful source. Visitors from the blog spend more time, view more pages and have a lower bounce rate than many traffic referral sources. And visitors from other blogs exhibit the same tendencies.
Make sure your company blog is indexed: The search engines can deliver great traffic. Make sure your blog is part of their search index database. For instance, here’s the Google page to submit your blog URL: http://www.google.com/addurl/?continue=/addurl
FriendFeed
FriendFeed is a lifestream aggregation service, which lets track all manner of information about other people from 59 different services. There is a good social aspect to FriendFeed, although the company is still pretty early in its lifecycle. So it’s likely that people in your industry aren’t yet active there.
But beside the social aspects, FriendFeed also has incredibly powerful information management tools. And it’s these tools that are valuable to the product marketer. I’m going to cover them below, but a more detailed description is available on this blog post.
Subscribe to people: Just like on Twitter, you can subscribe to people on FriendFeed, if they have an account there. When you do that, you’ll see there tweets, plus other useful information like Del.icio.us bookmarks, new blog posts, Google Reader shares, etc. You get a fuller picture of what is happening with those in your industry.
Subscribe to imaginary friends: Some people don’t have an account on FriendFeed, but they are active on some other site, like Twitter. But you can still stalk follow them on FriendFeed. You’re doing this not to interact with on FriendFeed, since they don’t have an account there. But I use FriendFeed as a master aggregator of people’s activity streams.
Track keywords in a Group: FriendFeed lets you create Group. Groups are containers into which you can pipe content from elsewhere. Use a Group to track keywords that relate to your industry.
For example, I’ve created the Innovation Management Group. Into that Group, I’m piping tweets with keywords I want to track, and SlideShare presentations and Del.icio.us bookmarks with tags I want to track. One centralized place to stay on top of what’s happening in my industry.
Put it all together into a List: FriendFeed has a feature called Lists. You can categorize the people you follow into different Lists. Then you can focus specifically on the activity streams of those people. I’m currently tracking the activity streams of 61 people associated with the Enterprise 2.0 industry. You can also add your keyword notification Room to your List. So you’ll see who’s talking about your industry beyond just those people you follow. As I wrote before, Follow Everything by a Select Few, Select Content by Everyone.
Track it in real-time: Once you have your industry List set up, FriendFeed provides a nice option. You can follow the activity streams in real-time as they hit the FriendFeed database. I find this to be important for two reasons. First, there are time people you know are tweeting something you care about. There’s an opportunity to do one of those @reply engagements. You don’t want to wait until the end of the day to see that, because the moment is lost. The second reason is that stuff collects, and if you wait until the end of the day you’re less likely to catch things of interest.
As I wrote in another post, it’s really not that distracting to track activity streams this way. An alternative people use for real-time flow and user groups is Tweetdeck. It’s only for Twitter, but many swear by it.
Connecting the dots: Once you’re set-up with with your List + keyword tracking Room + real-time, something amazing happens. You will start to understand what people are buzzing about more. You’ll see recurring themes. You learn who people in your industry are paying attention to. You see the relationships that exist among industry folks, via the @reply conversations. You’ll know which conferences and trade shows are most talked about.
SlideShare, Scribd
SlideShare and Scribd are the two leading social document sharing sites. Social document sharing? Huh? What you do is upload a document to these sites, and others who are doing research can find and read them. Document types include:
- PowerPoints
- Word Documents
- PDFs
- Spreadsheets
These are great places to share the content you’re creating. Let me give you an example of how this worked for me.
In November 2008, I put on a webinar titled How to Double the Value of Your Social Software. Afterwards, I put the presentation on SlideShare. In the two months since it’s been there, the following has happened:
A more recent presentation for a Spigit webinar, Tapping Communities to Accelerate Corporate Innovation, has been viewed 1,508 times.
I recently added the social software presentation to Scribd, and it now has 586 views and two Likes.
I assure you, the after-webinar action is much greater than that which occurred with the webinar itself. The effect of all this is to get your company’s point of view into the market. You are a contributor to the industry dialogue, and your company is very relevant in the thinking about the industry’s future. As I said, this is particularly important for smaller companies, who cannot rely on a huge market presence to ensure getting people’s attention. But even the big companies benefit from this.
This is product marketing, social media style.
Considerations for SlideShare, Scribd: As you can see, the webinar presentation can actually multiply in value when it’s on these social document sharing sites. I know Guy Kawasaki has the 10/20/30 Rule of PowerPoint. Consider that a philosophy, not a rule. What I take from his blog post is the advice not clutter up your slides with too much.
When people are viewing your PowerPoint, they will not have the advantage of your voiceover. You can’t provide a spare slide with just a picture and hope everyone gets what you’re saying. In the webinar, you’ll have a nice narration for the slide. In SlideShare and Scribd, each slide has to stand on its own. Here are my tips:
- Minimize the times custom animation is a requirement to talk about the slide. Because customer animation doesn’t work on these sites.
- Pictures and graphics – these break the monotony of endless bullets and text
- Each slide should have two messages: (1) the point/data of the slide; (2) a way to provide your commentary to that point/data
- Assuming multiple sections, recap the slides of each section – make sure the point is made
And don’t forget to tag, tag, tag your presentations. Don’t be chary with the tags. People will use them to find your documents. Of course, make sure your tags actually reflect the material in the presentation.
As you go into a webinar, think about your presentation being consumed by an audience many times bigger than the number of attendees to the webinar.
YouTube, Google Video
Videos are a popular way for people to view content. A part of your product marketing job may include producing canned demos of the product. These can be on your company website. And they can go on YouTube as well.
I’ve uploaded three demos for Connectbeam to YouTube. In total, they’ve gotten 380 views. Not quite the same as the SlideShare or blog posts. But it’s nice incremental exposure for something you’re creating anyway.
There are countless stories of videos going viral, and it’s a holy grail for marketers. But I don’t spend a lot of time on that. If you happen to have a particular strength in entertaining videos, by all means take advantage of it.
One limitation for YouTube is that videos’ running time can be no longer than 10:59. For basic product demos, this should be more than enough time. But for webinars, which can run an hour, YouTube doesn’t work.
Google Video supports much longer videos. It’s where I uploaded the recorded webinar from November. It’s not nearly as social as YouTube, but it does come up in Google search results.
Unfortunately, Google is going to stop accepting new uploads to Google Video in a few months.
However, assuming you do get a video to Google Video or you upload shorter media to YouTube, you can embed these videos in a blog post and give them color commentary to spur viewing.
Use high quality resolution when embedding YouTube videos: The normal resolution of a YouTube video is rough. This may be something that happens when you convert a Camtasia video to a YouTube-acceptable format. But you should know about this, because it hurts the viewing quality of the video. Those web screenshots can be hard to read.
Fortunately, there is a solution to this. When you embed a YouTube video on a web page or blog post, you can alter the embed code to force the video to view in high resolution. The hack described in this blog post works. It will ensure that the video’s fidelity is much higher, making it a more enjoyable viewing experience.
Wrapping Up
A site that I think could be more valuable to engage in is LinkedIn. There are groups and questions that people pose. I haven’t been very active there, but it’s worth a look. Depending on your industry, Facebook may also have value.
I hope this post has been helpful. I seriously could triple the size of this post, but it’s long enough. If you want to talk more about this, feel free to reach out to me on email: (hutch <dot> carpenter at gmail <dot> com) or on the phone 415-377-3610.
Finally, here are a couple relevant posts as follow-up:
I encourage you to get out there and start experimenting. It’s the best way to learn.
[tweetmeme source=”bhc3″]













The Conversation